

Consequently, it will have a negative charge on one face and a positive charge on the opposing face. For example, when a crystal’s charge balance is impacted by 10 percent, it generates electricity. Due to the force that’s applied, the material’s charge balance changes. As such, the force needs to be applied with the utmost care. What’s key to understand is that the energy applied to a material can be a knock, squeeze, tap or other force that impacts the material but doesn’t fracture it.
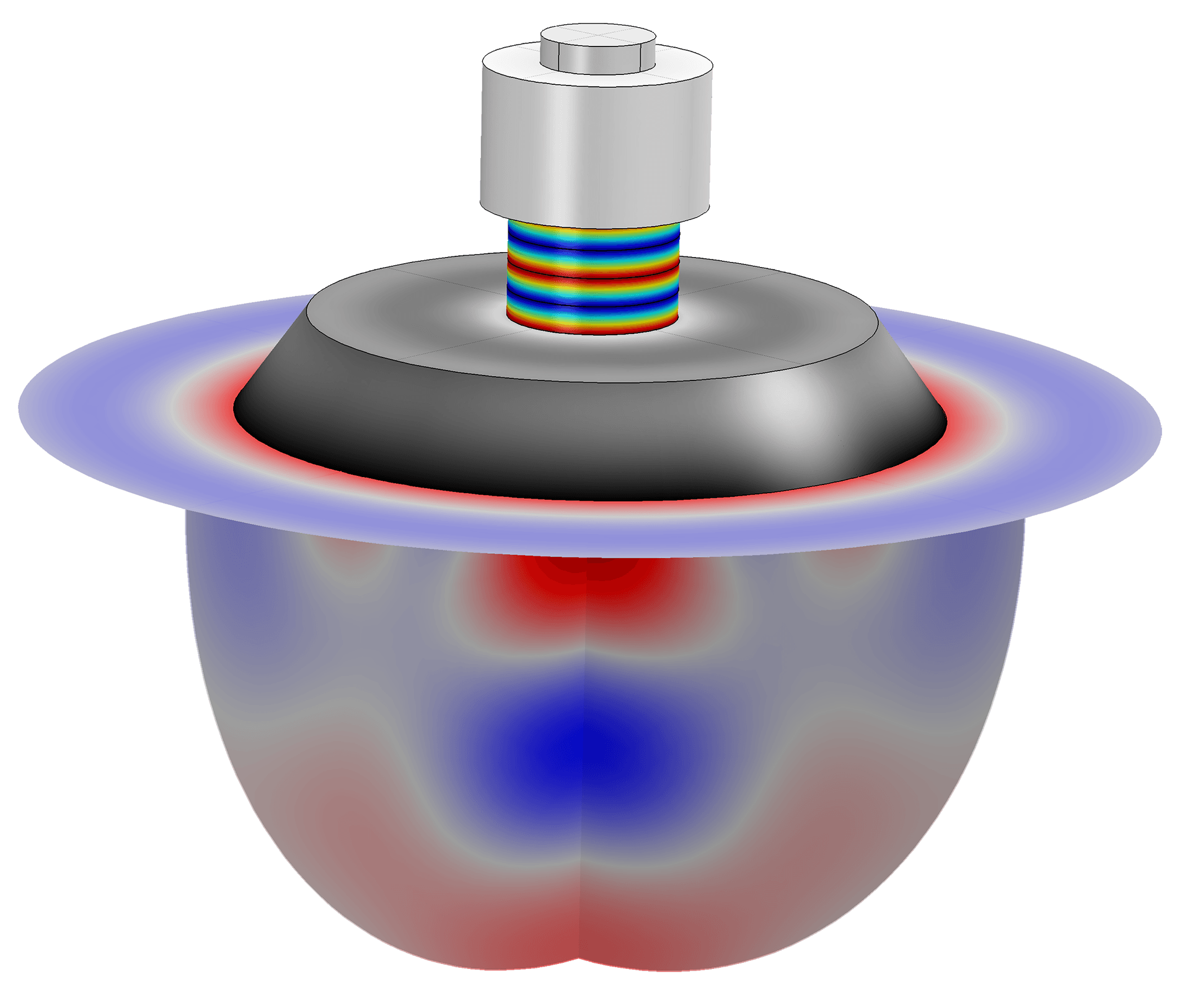
Tension and compression generated voltages of opposite polarity, and in proportion to the applied force. In 1880, French physicists Jacques and Pierre Curie - who appeared to be brothers- discovered an unusual characteristic of certain crystalline minerals: when subjected to a mechanical force, the piezoelectric crystals became electrically polarized. The resulting effect is a type of electricity produced because of pressure and/or latent heat - otherwise known as piezoelectricity. Literally translated, “piezoelectricity” refers to electricity that’s the result of the application of latent heat and pressure.ĭue to the application of mechanical stresses, an electric charge can build up in a number of solid materials, including select ceramics, crystals and some biological materials like DNA, bone and certain proteins. The term “piezoelectricity” has its roots in the Greek words for “press” and “amber” - which historically has been used as a source of electricity.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
